Deep Venous Thrombosis
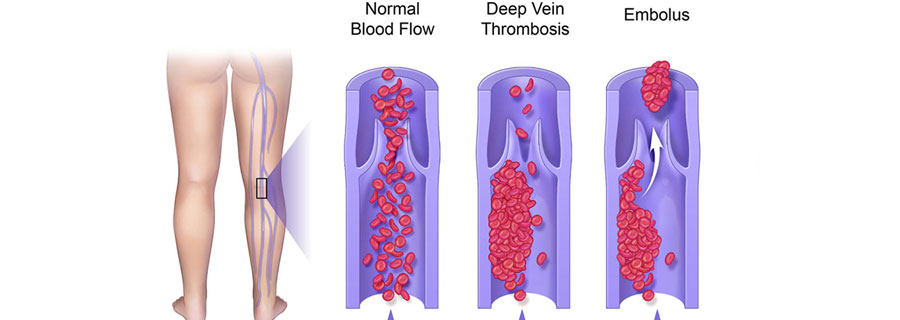
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins, usually in the legs. DVT is a significant medical concern as it can lead to serious complications if not promptly diagnosed and treated.
Causes and Risk Factors:
DVT typically occurs when blood flow becomes sluggish or stagnant, leading to the formation of a blood clot. Several factors can increase the risk of developing DVT, including:
- Prolonged Immobility: Long periods of immobility, such as during long flights, bed rest after surgery, or extended periods of sitting, can increase the risk of DVT.
- Surgery or Trauma: Surgery, especially procedures involving the legs or pelvis, can disrupt normal blood flow and increase the risk of clot formation. Trauma or injuries to the legs can also contribute to clot development.
Symptoms:
In some cases, DVT may not cause noticeable symptoms. When symptoms are present, they can include:
- Swelling in one leg (usually below the knee)
- Pain or tenderness in the affected leg, which may worsen with walking or standing.
- Warmth and redness over the area of the clot
